Chapter 32. Scroll-bars
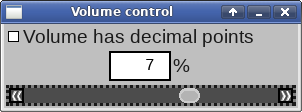
Widgets that scroll, such as multi-line
input fields,
provide their own scroll-bars.
Scroll-bars are also useful on their own:
they are an intuitive way to set a value in some
specified range.
A factory's create_horizontal_scrollbar()
and create_vertical_scrollbar() methods
create new, stand-alone, independent
x::w::scrollbars.
scrollbar.C creates a scroll-bar below a
checkbox and an
input field.
The scroll-bar supposedly controls a volume value of some sort, which
can be set to a range of 0 through 11.
As the scroll-bar's value gets adjusted, the input field above it
reflects the updated volume value. A new value can be explicitly typed
into the input field, and this manually moves the scrollbar.
The checkbox adds (or removes) a decimal point, making the scrollbar's
value range from 0.0 through 11.0.
/* ** Copyright 2017-2021 Double Precision, Inc. ** See COPYING for distribution information. */ #include "config.h" #include <x/mpobj.H> #include <x/exception.H> #include <x/destroy_callback.H> #include <x/ref.H> #include <x/obj.H> #include <x/weakcapture.H> #include <x/appid.H> #include <x/w/main_window.H> #include <x/w/label.H> #include <x/w/gridlayoutmanager.H> #include <x/w/gridfactory.H> #include <x/w/scrollbar.H> #include <x/w/image_button.H> #include <x/w/input_field.H> #include <x/w/container.H> #include <x/w/key_event.H> #include <x/w/dialog.H> #include "close_flag.H" #include <string> #include <string_view> #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <sstream> #include <cmath> std::string x::appid() noexcept { return "scrollbar.examples.w.libcxx.com"; } // Need an object to keep track of some metadata, that can be captured // by several callbacks. class volume_infoObj : virtual public x::obj { public: bool use_decimals=false; double current_volume=0; // Return a scrollbar that ranges 0-11, or 0-110. auto scrollbar_config() const { x::w::scrollbar_config config{12, 1}; if (use_decimals) { config.range=120; config.page_size=10; config.value=(int)std::round(current_volume * 10); } else { config.value=(int)current_volume; } config.minimum_size=75; // 75 millimeters wide. return config; } void set_volume(double v, const x::w::input_field &input_field) { current_volume=use_decimals ? v/10:v; std::ostringstream o; if (use_decimals) o << std::fixed << std::setprecision(1); o << current_volume; input_field->set(o.str()); } void set_volume(const x::w::input_field &input_field, const x::w::scrollbar &scrollbar, const x::w::main_window &main_window) { std::string current_volume=x::w::input_lock{input_field}.get(); std::istringstream i{current_volume}; double v; if ( (i >> v) && i.get() == std::istream::traits_type::eof()) { if (use_decimals) v *= 10; int n=std::round(v); if (n >= 0 && n <= (use_decimals ? 110:11)) { scrollbar->set(n); return; } } // Bad input. Show an error dialog. auto d=main_window->create_ok_dialog ({"error@scrollbar.examples.w.libcxx.com", true}, "alert", [] (const x::w::factory &f) { f->create_label("Bad input"); }, main_window->destroy_when_closed ("error@scrollbar.examples.w.libcxx.com")); d->dialog_window->set_window_title("Error"); main_window->set_window_class ("main", "scrollbar.examples.w.libcxx.com"); d->dialog_window->show_all(); } void set_decimals(const x::w::input_field &input_field, const x::w::scrollbar &scrollbar) { scrollbar->reconfigure(scrollbar_config()); set_volume(current_volume, input_field); } }; typedef x::ref<volume_infoObj> volume_info; void initialize_volume_control(const x::w::main_window &main_window) { auto layout=main_window->gridlayout(); x::w::gridfactory factory=layout->append_row(); auto vi=volume_info::create(); x::w::image_button checkbox= factory->create_checkbox([] (const auto &f) { f->create_label("Volume has decimal points"); }); factory=layout->append_row(); // Create an input_field, with a '%' immediately afterwards. Center it // because the scrollbar will be below it, and wider. For doing this, // we'll create an inner container, that's centered. factory->halign(x::w::halign::center); x::w::input_fieldptr input_fieldptr; factory->create_container ([&] (const auto &container) { auto glm=container->gridlayout(); glm->row_alignment(0, x::w::valign::middle); auto row=glm->append_row(); // Don't need any padding, the main grid default // padding will suffice. row->padding(0); x::w::input_field_config config{5}; config.alignment=x::w::halign::right; input_fieldptr=row->create_input_field("0", config); row->create_label("%"); }, x::w::new_gridlayoutmanager{}); x::w::input_field input_field=input_fieldptr; factory=layout->append_row(); x::w::scrollbar sb= factory->create_horizontal_scrollbar(vi->scrollbar_config(), [vi, input_field] (ONLY IN_THREAD, const x::w::scrollbar_info_t &status) { vi->set_volume(status.dragged_value, input_field); }); // Add a key event to the input field, for the Enter key, to set the // manually typed-in value as the explicit value. input_field->on_key_event([vi, fields=x::make_weak_capture(sb, input_field, main_window)] (ONLY IN_THREAD, const auto &why, bool activated, const auto &ignore) { // Verify that that a key_event gets // passed in. if (!std::holds_alternative<const x::w::key_event *>(why)) return false; auto ke=std::get<const x::w::key_event *>(why); if (ke->unicode != '\n') return false; if (!activated) return true; auto got=fields.get(); if (got) { auto & [sb, input_field, main_window] = *got; vi->set_volume(input_field, sb, main_window); } return true; }); checkbox->on_activate([vi, fields=x::make_weak_capture(sb, input_field)] (ONLY IN_THREAD, size_t state, const auto &ignore1, const auto &ignore2) { vi->use_decimals=state > 0; auto got=fields.get(); if (got) { auto &[sb, input_field]=*got; vi->set_decimals(input_field, sb); } }); } void testscrollbar() { x::destroy_callback::base::guard guard; auto close_flag=close_flag_ref::create(); auto main_window=x::w::main_window ::create([&] (const auto &main_window) { initialize_volume_control(main_window); main_window->set_window_title("Volume control"); main_window->show_all(); }); guard(main_window->connection_mcguffin()); main_window->on_disconnect([] { exit(1); }); main_window->on_delete ([close_flag] (ONLY IN_THREAD, const auto &ignore) { close_flag->close(); }); close_flag->wait(); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { try { testscrollbar(); } catch (const x::exception &e) { e->caught(); exit(1); } return 0; }
Creating and configuring scroll-bars
scrollbar.C uses
a factory's create_horizontal_scrollbar()'s to
create a new scroll-bar, and shows some examples of using it.
An x::w::scrollbar_config
parameter
specifies scroll-bar's configuration, and gets passed to
create_horizontal_scrollbar() or
create_vertical_scrollbar().
An existing scroll-bar's reconfigure() method
updates its configuration.
create_horizontal_scrollbar() and
create_vertical_scrollbar() take the
following optional parameters. Either parameter is optional, but
they must appear in the following order if both are present:
The scroll-bar's initial callback that gets executed to report changes to the scroll-bar's position. An existing scroll-bar's
on_update() method installs a new callback, replacing the previous one.A
x::w::const_scrollbar_appearanceobject that set a custom visual scrollbar appearance.
x::w::scrollbar_config's
minimum_size sets the scroll-bar's minimum size,
in millimeters.
The scroll-bar's layout manager typically sizes the scroll-bar to
fit within its assigned cell, and this value instructs the layout
manager what the minimum size should be.
If scrollbar.C does not specify its scrollbar's
width, it becomes the size of the short label above it.
As such, the scroll-bar's minimum width is slightly larger, and
the scrollbar.C creates a larger window on account
of that.
Scroll-bars are focusable widgets, and they respond to the following keys when they have the keyboard focus:
Cursor-Left and Cursor-Up keys move the scroll-bar towards its left or upper end (smaller scroll-bar values). Cursor-Right and Cursor-Down keys move the scroll-bar towards its right or lower end (larger scroll-bar values). The scroll-bar's value gets adjusted by the
x::w::scrollbar_config'sincrement; in combination with the Ctrl key the scroll-bar's value gets incremented or decremented by 1.Page-Up and Page-Down move the scroll-bar in the appropriate direction. The scroll-bar's value gets adjusted by the
x::w::scrollbar_config'spage_size.
Note
It's possible for a
x::w::scrollbar_config's
minimum_size to be smaller than the
minimum size that's needed to meaningfully draw all of its
inner controls, subsequently the scroll-bars can get resized
to a very small size, accordingly.
When that happens the scroll-bars temporarily disable
themselves from receiving keyboard focus.
The reason for this is to avoid visual confusion when the
keyboard focus seems
to disappear (the scroll-bar's keyboard focus frame is so small
that it's hard to see or there may not be even enough pixels
to draw them).
The small scroll-bars remain disabled until their size is sufficient
to fully draw them, and they'll automatically reenable themselves.
This is combined with scroll-bars'
set_enabled() method (that all
focusable widgets have). Scroll-bars have enabled keyboard
focus if they are both set_enabled() and
are big enough for their drawn contents.